Brown Rice Nutrition – Benefits and Side Effects
Table of Contents
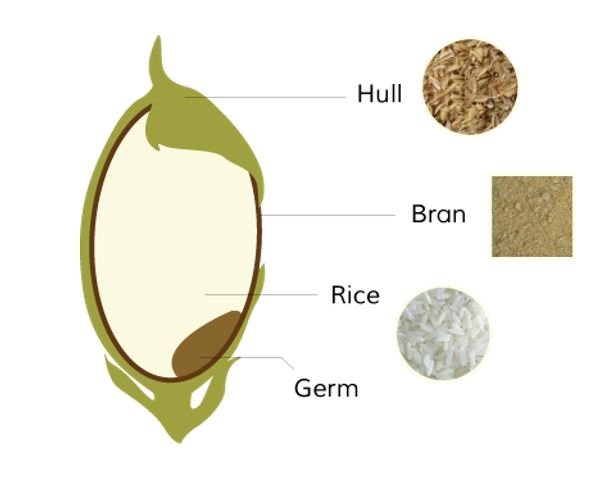
What is brown rice? brown rice nutrition
Brown rice is ‘rice grain’ without the hull. Whereas white rice is rice grain without hull, bran, and germ. Brown rice contains more nutrients (vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, etc.) because of retaining bran and germ. brown rice nutrition
Brown Rice Nutritional Facts – 100 g (source)
| Nutritional Facts (100g) | Brown Rice | White Rice | Daily Requirement Male, age 30 |
| Calories | 111 | 130 | 2484 |
| Carbs | 23 g (Dietary fiber-1.8 g) | 28.2 g (Dietary fiber- 0.4 g) | 130 g (Dietary fiber- 38 g) |
| Protein | 2.6 grams | 2.7 grams | 48 grams |
| Fat | 0.9 grams | 0.3 grams | 30-50 grams |
| Vitamine K | 0.6 mg | 0.0 mg | 120 mg |
| Thiamin (B1) | 0.1 mg | 0.2 mg | 1.2 mg |
| Niacin (B3) | 1.5 mg | 1.5 mg | 16 mg |
| Pyridoxine (B6) | 0.1 mg | 0.1 mg | 1.3 mg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) | 0.3 mg | 0.4 mg | 5 mg |
| Calcium | 10.0 mg | 10.0 mg | 1000 mg |
| Iron | 0.4 mg | 1.2 mg | 8 mg |
| Magnesium | 43 mg | 12 mg | 400 mg |
| Phosphorus | 83 mg | 43 mg | 700 mg |
| Zinc | 0.6 mg | 0.5 mg | 11 mg |
| Copper | 0.1 mg | 0.1 mg | 0.9 mg |
| Manganese | 0.9 mg | 0.5 mg | 2.3 mg |
| Selenium | 9.8 mcg | 7.5 mcg | 55 mcg |
Health Benefits of Brown Rice
Helps in weight loss and diabetes: Study shows that substitution of whole grains, including brown rice, for white rice may lower risk of type 2 diabetes. Consumption of Brown rice in place of White rice can help reduce 24-h glucose and fasting insulin responses among overweight Asian Indians (Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics).
Heart Disease: Brown rice also helps fight heart disease because of presence of large amount of plant lignans.
Rich on Magnesium: Brown rice contains good amount of Magnesium which is vital to our body. Magnesium deficiency can cause a wide variety of features including hypocalcaemia, hypokalaemia and cardiac and neurological manifestations.
Lowers Cholesterol: Studies have shown that the rice bran and fiber contained in brown rice may be able to lower unhealthy cholesterol levels, particularly LDL cholesterol. The fiber in brown rice naturally aids in lowering cholesterol levels in the body.
Anticancer: Some of the phytochemicals and minerals found in whole grains may be associated with a lower risk of certain cancers.
Boost Immunity: Research study shows that pre-germinated brown rice could enhance maternal mental health and immunity during lactation.
Antioxidants: Brown rice is rich in antioxidants that help to protect against damage caused by oxygen free radicals.
Gallstones: Studies have shown that the insoluble fiber present in brown rice helps to cut down the risk of gallstones (refer).
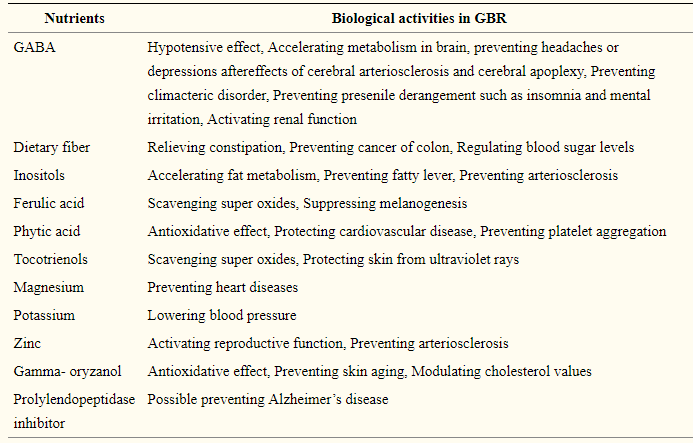
Essential Nutrients Role in Brown Rice
Fighting with the side effects of Brown Rice
Eat in moderation: It is always better to eat anything in a limit. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations warns that, “Rice in particular, can take up more arsenic than other foods and due to its high consumption can contribute significantly to arsenic exposure.
Soak before use: Most whole grains including brown rice has phytic acid that limits the absorption of vitamins and minerals causing adverse health effects and nutrient deficiency. That is why it is advised to soak whole grains that activate phytase enzyme which in turn reduces the phytic acid.